Cell biology is a fascinating and complex field that explores the structure and function of cells, the basic units of life. Understanding cell biology is essential for a wide range of disciplines, including medicine, genetics, and biotechnology. In this article, we will explore the basics of cell biology, including the structure of cells and their various functions.
What is a Cell?
Cells are the smallest structural and functional units of living organisms. They are often referred to as the “building blocks of life” because all living things are composed of one or more cells. Cells vary in size, shape, and function, but they all have certain features in common.
Cell Structure
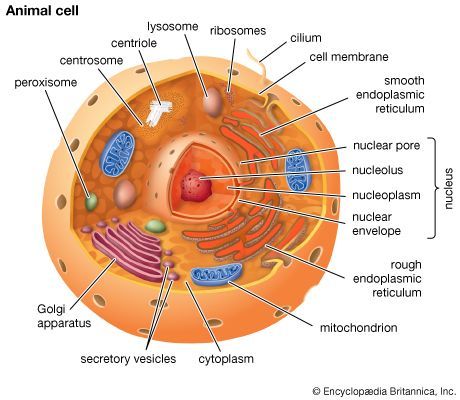
Cells are enclosed by a cell membrane, which serves as a barrier between the cell’s internal environment and the external environment. Inside the cell membrane is the cytoplasm, a gel-like substance that contains various organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Nucleus: The nucleus is often referred to as the “control center” of the cell. It contains the cell’s genetic material, including DNA, which carries the instructions for making proteins and other important molecules.
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are known as the “powerhouses” of the cell because they produce the energy needed for cell functions through a process called cellular respiration.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that is involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and other important cellular processes.
Cell Function
Cells perform a wide range of functions that are essential for life. Some of the key functions of cells include:
Metabolism: Cells take in nutrients from the environment and use them to produce energy through various metabolic processes.
Growth and Reproduction: Cells grow and divide to produce new cells, allowing organisms to grow and reproduce.
Homeostasis: Cells maintain a stable internal environment through processes such as temperature regulation and waste removal.
Types of Cells
There are several different types of cells in the human body, each with specialized functions. Some of the main types of cells include:
Red Blood Cells: Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and remove carbon dioxide from the body.
Neurons: Neurons are specialized cells that transmit electrical signals throughout the body, allowing for communication between different parts of the body.
White Blood Cells: White blood cells are part of the immune system and help defend the body against infections and diseases.
Cell Communication
Cells communicate with each other through a process known as cell signaling. Cell signaling involves the release of signaling molecules, such as hormones or neurotransmitters, which bind to receptors on the surface of target cells and trigger a response. This communication is essential for coordinating the activities of different cells within an organism.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of cell biology is essential for any individual interested in the life sciences or related fields. Cells are the building blocks of life, and their structure and function are crucial for maintaining the health and functionality of living organisms. By exploring the structure and function of cells, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the natural world.
Cell biology is a dynamic and ever-evolving field, with new discoveries being made all the time. By studying cells and their various functions, scientists can unlock the secrets of life and develop new treatments for a wide range of diseases. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply a curious individual, the world of cell biology offers endless opportunities for exploration and discovery.