Understanding bonding and molecular structure is fundamental to grasping the basics of chemistry. In this article, we will break down these concepts for beginners in a clear and concise manner.
Types of Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in a compound. There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic.
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds form when one atom donates an electron to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions that attract each other. This type of bond typically occurs between a metal and a nonmetal.
Covalent Bonds
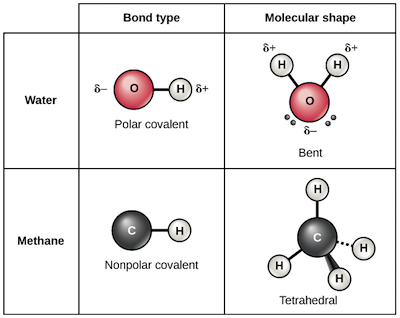
Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration. This type of bond typically occurs between nonmetal atoms.
Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds occur in metals, where the outer electrons of the atoms are free to move throughout the structure, creating a “sea of electrons” that hold the metal atoms together.
Molecular Structure
Molecular structure refers to the arrangement of atoms within a molecule. The shape of a molecule is determined by the arrangement of its atoms and the bonding between them.
Types of Molecular Structures
There are several different types of molecular structures, including linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, and bent. The shape of a molecule is important because it affects its properties and reactivity.
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction between molecules. These forces are weaker than chemical bonds but still play a crucial role in determining the physical properties of substances.
Types of Intermolecular Forces
There are three main types of intermolecular forces: London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding. These forces influence properties such as boiling and melting points, solubility, and viscosity.
Importance of Understanding Bonding and Molecular Structure
Understanding bonding and molecular structure is essential in various fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. It allows scientists to predict the properties and behaviors of substances, design new materials, and develop drugs and treatments.
Conclusion
Bonding and molecular structure are fundamental concepts in chemistry that form the basis of understanding how atoms interact to form compounds and substances. By mastering these concepts, beginners can gain a solid foundation in chemistry and pave the way for further learning and exploration in the field.
Keep exploring and learning, and you will uncover the fascinating world of bonding and molecular structure!
References:
Chemistry: The Central Science by Brown, LeMay, Bursten, Murphy, and Woodward
Chemical Principles by Steven S. Zumdahl and Susan A. Zumdahl