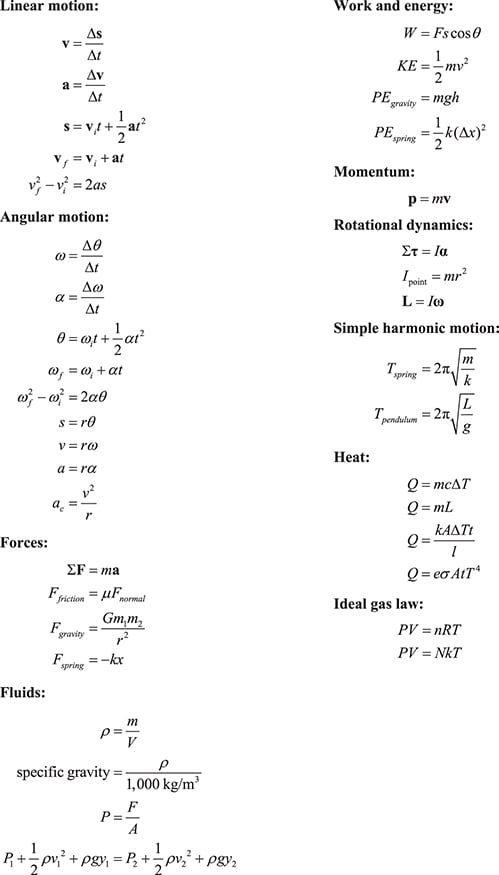
Physics is a fundamental subject that is crucial in understanding how the world works. It is the study of matter, energy, and the interactions between them. One of the key components of mastering physics is understanding and applying the various formulas that govern the behavior of physical phenomena. Mastery of these formulas not only helps students excel in their physics courses but also sets a strong foundation for any future endeavors in the field of science and technology.
Newton’s Laws of Motion
One of the most fundamental concepts in physics is Newton’s Laws of Motion. These three laws describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. They are essential in understanding the behavior of objects in motion and are the basis for many other physics principles.
First Law: An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
Second Law: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass (F=ma).
Third Law: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Kinematic Equations
Kinematic equations describe the motion of objects in terms of distance, time, velocity, and acceleration. These equations are crucial in solving problems involving motion and are essential for any physics student to master.
Equation 1: v = u + at (final velocity = initial velocity + acceleration x time)
Equation 2: s = ut + 0.5at^2 (distance = initial velocity x time + 0.5 x acceleration x time^2)
Equation 3: v^2 = u^2 + 2as (final velocity^2 = initial velocity^2 + 2 x acceleration x distance)
Electromagnetic Formulas
Electromagnetic formulas describe the relationship between electric and magnetic fields and are crucial in understanding the behavior of charged particles and electromagnetic waves.
Coulomb’s Law: F = kq1q2/r^2 (the force between two charged particles is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them)
Ohm’s Law: V = IR (the voltage across a resistor is equal to the current flowing through it multiplied by its resistance)
Magnetic Field Strength: B = μ0I/2πr (the magnetic field strength at a distance r from a current-carrying wire is directly proportional to the current and inversely proportional to the distance)
Thermodynamics Formulas
Thermodynamics formulas describe the relationship between heat, temperature, and energy transfer. These formulas are essential in understanding processes such as heat conduction, convection, and radiation.
First Law of Thermodynamics: ΔU = Q – W (the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system)
Second Law of Thermodynamics: ΔS ≥ Q/T (the entropy of a system increases or remains constant in any process)
Heat Transfer Equation: Q = mcΔt (the heat transfer between two substances is equal to the mass of the substance, specific heat capacity, and change in temperature)
Conclusion
Mastering physics formulas is essential for any student studying physics. These formulas provide a foundation for understanding the laws of nature and how they govern the behavior of physical phenomena. By consistently practicing and applying these formulas, students can develop a strong understanding of physics and excel in their academic pursuits. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t hesitate to work through problems and seek help when needed. With dedication and perseverance, you can become a physics whiz in no time!