The second law of” width=”632″ height=”608″>
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of energy and its transformations in various systems. It is a fundamental discipline in the field of engineering and plays a crucial role in the design and operation of many technologies and devices.
The Laws of Thermodynamics
First Law: Conservation of Energy
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In other words, the total energy in a closed system remains constant over time. This law is the basis for understanding how energy flows within a system and is essential for designing efficient energy systems.
Second Law: Entropy
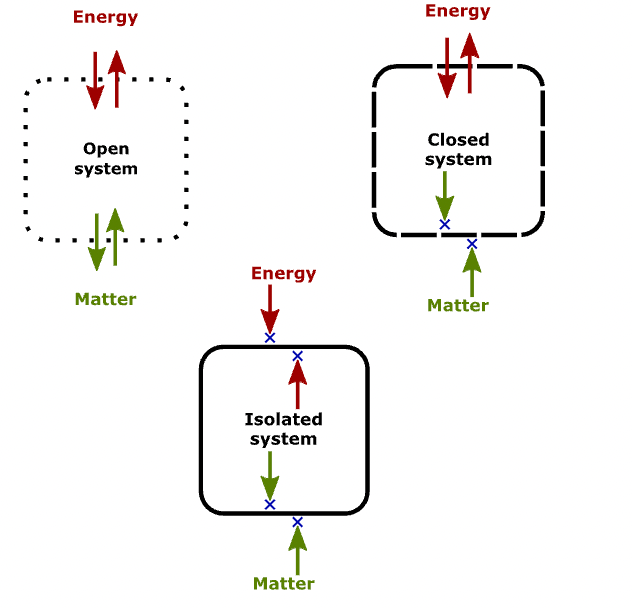
The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time. Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system, and this law explains why processes tend to move towards a state of greater disorder. It also provides insights into the efficiency of energy conversion processes.
Applications of Thermodynamics
Thermal Power Plants
Thermodynamics plays a crucial role in the operation of thermal power plants, which generate electricity by converting heat energy into mechanical energy. The principles of thermodynamics are used to optimize the efficiency of power generation and minimize energy losses in the system.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
Thermodynamics is also essential in the design and operation of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. These systems work by removing heat from a space and transferring it to another location, and the laws of thermodynamics govern the heat transfer processes that make this possible.
Chemical Engineering
In the field of chemical engineering, thermodynamics is used to analyze and optimize chemical processes. Understanding the thermodynamic properties of substances helps engineers design efficient processes for producing chemicals, fuels, and other products.
Conclusion
Thermodynamics is a fundamental discipline that underpins many aspects of modern technology and engineering. The laws of thermodynamics provide a framework for understanding how energy behaves in different systems, and their applications are widespread in various industries. By applying the principles of thermodynamics, engineers can design more efficient and sustainable technologies that meet the challenges of the modern world.